Ancient exoplanet discovery boosts chances of finding alien life

Among the vital variables in determining the likelihood that alien life exists somewhere else in our galaxy is the variety of stars that have planetary systems, and also the proportion of those earths that might be suitable for life.
So the exploration of no less than 5 sub-Earth-sized exoplanets orbiting an old star, Kepler-444, which is not also distant from our own planetary system, has significant ramifications for the possibility we may eventually face ET.
Formed over 11-billion years earlier, the Kepler-444 system shows that such tiny planets have existed through the majority of the background of our world. And the more little worlds that exist, the higher the opportunities that one of them (or one of their moons) might being in the supposed “Goldilocks area” that enables life to exist.
This exceptional exploration was enabled not only by the space-based NASA Kepler telescope but also a technique called asteroseismology.
Kepler continuously measured the illumination of more than 150,000 stars for 4 years. As worlds orbit in front of the stellar disc they cause tiny dips in the brightness of the celebrity, yielding info on earth’s orbital period as well as size relative to the size of their host star
Greater than 1,800 exoplanets have been discovered to date, consisting of some Earth-sized planets in the habitable area. Such discoveries have demonstrated that worlds with good conditions permanently may in fact be common.
Yet the age of the host celebrities– and also for that reason the age of the earths– was frequently unknown. This is since the hints that give a hint to the age of a celebrity tend to be concealed under its visible surface.
Using asteroseismology to date a star.
Luckily, the variability in the illumination of celebrities offers a means to settle this problem utilizing asteroseismology.
Stars with similar and cooler temperature levels than our sun transportation power to their surface with the up-flow as well as down-flow of gas that streams due to the interplay of buoyancy and gravity. The turbulent activity of the gas thrills stress waves to travel via the outstanding interior.
The frequency of these waves– likewise described as oscillations– are determined by the audio rate, which subsequently depends upon the outstanding indoor framework and also structure.
These oscillations likewise travel to different depths within the celebrity, thereby offering a method to probe the structure by observing the oscillations. As the core properties of the star change with time, such changes are inscribed in the oscillation frequency patterns.
Conveniently, we can measure outstanding oscillations using the very same information we utilize to find transiting planets. Thus we were able to use asteroseismology to study a remarkable planetary system in elegant information and to establish the age of the host celebrity.
Kepler-444: An old research laboratory for worldly as well as stellar astrophysics
At a distance of simply 120 light years, Kepler-444 is slightly cooler than our sunlight. It is likewise light on hefty components and also shows a huge noticeable activity on the night skies. These homes make it a member of the “thick disc,” a stellar populace of old celebrities believed to border celebrities closer to the galactic aircraft, including our sun.
All this already made Kepler-444 an interesting star to examine on its own. But when the Kepler team found transportations of five worlds, it was clear that this was a really special discover.
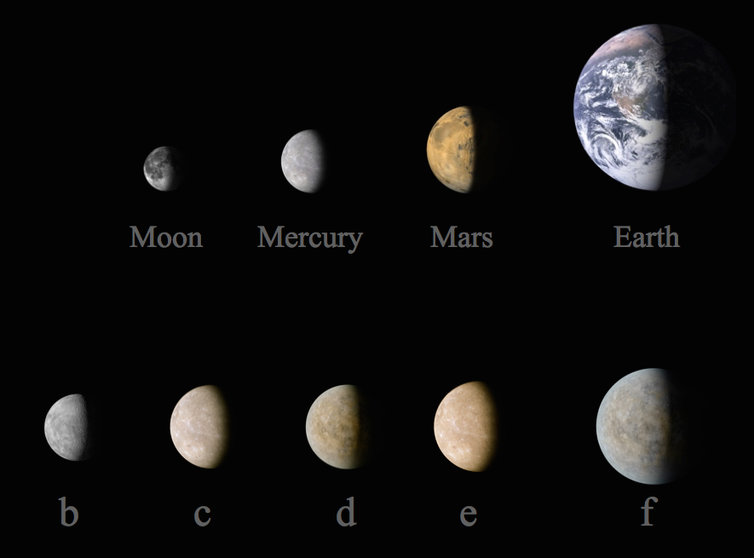

Further analysis of the Kepler information disclosed greater than 30 oscillation frequencies in the host celebrity. Using these frequencies, the age of Kepler-444 was nailed down to 11.2 +/- 1-billion years. With cosmology dating the big bang back to 13.8 billion years, this suggests that the Kepler-444 worlds created when deep space was only one fifth of its existing age.
All Kepler-444 planets have sizes between that of Mercury and also Venus, with the smallest planet having its span measured with a precision to the nearby 100 kilometres. Although their masses are as yet unidentified, the tiny earth sizes suggest that they are most likely rocky, similar to the terrestrial planets– Mercury, Venus, Earth as well as Mars– in our planetary system.
Unlike our solar system, nevertheless, the Kepler-444 earths orbit their host celebrity in less than 10 days. Even taking into consideration the cooler temperature level of Kepler-444 compared to our sunlight, this places these old worlds well outside the habitable zone.
Despite the rather hostile setting, Kepler-444 notes an essential milestone to recognize whether life might be common outside the planetary system. While the Kepler objective has actually formerly demonstrated that tiny worlds are abundant, Kepler-444 confirms that such earths have actually developed for a lot of the background of our cosmos.
If life can form on Earth-sized planets in the habitable zone of various other stars, this indicates that it may have based on distant worlds long prior to life emerged right here on Earth.
