MELAS syndrome
Mitochondrial encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like episodes (MELAS) is one of the family of mitochondrial diseases, which also include MERRF syndrome, and Leber’s hereditary optic neuropathy. It was first characterized under this name in 1984. A feature of these diseases is that they are caused by defects in the mitochondrial genome which is inherited purely from the female parent.
MELAS is a condition that affects many of the body’s systems, particularly the brain and nervous system (encephalo-) and muscles (myopathy). In most cases, the signs and symptoms of this disorder appear in childhood following a period of normal development. Children with MELAS often have normal early psychomotor development until the onset of symptoms between 2 and 10 years old.
Though less common, infantile onset may occur and may present as failure to thrive, growth retardation and progressive deafness. Onset in older children typically presents as recurrent attacks of a migraine-like headache, anorexia, vomiting, and seizures. Children with MELAS are also frequently found to have short stature.
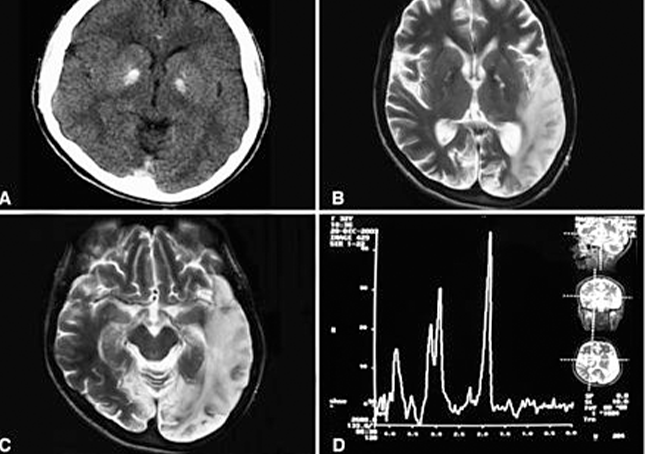
Most people with MELAS have a buildup of lactic acid in their bodies, a condition called lactic acidosis. Increased acidity in the blood can lead to vomiting, abdominal pain, extreme tiredness (fatigue), muscle weakness, loss of bowel control, and difficulty breathing. Less commonly, people with MELAS may experience involuntary muscle spasms (myoclonus), impaired muscle coordination (ataxia), hearing loss, heart and kidney problems, diabetes, epilepsy, and hormonal imbalances.
The presentation of some cases is similar to that of Kearns–Sayre syndrome.
Myoclonus epilepsy associated with ragged red fibers (MERRF) may be confused with MELAS as they both involve seizures, mental deterioration, and myopathy with ragged red fibers on biopsy. MERRF patients may also have hearing loss, visual disturbance secondary to optic atrophy, and short stature. The characteristic myoclonic seizure in MERRF may help to narrow diagnosis, but genetic testing should be considered to distinguish the 2 conditions.
Leigh syndrome may also present with progressive neurological deterioration, seizures, and vomiting mainly in young children.
