Climate change and agriculture
Climate change and agriculture are interrelated processes, both of which take place on a global scale, with the adverse effects of climate change affecting agriculture both directly and indirectly.
This can take place through changes in average temperatures, rainfall, and climate extremes (e.g., heat waves); changes in pests and diseases; changes in atmospheric carbon dioxide and ground-level ozone concentrations; changes in the nutritional quality of some foods; and changes in sea level.
Climate change is already affecting agriculture, with effects unevenly distributed across the world. Future climate changes will most likely affect crop production in low latitude countries negatively, while effects in northern latitudes may be positive or negative. Animal husbandry also contributes towards climate change through greenhouse gas emissions.
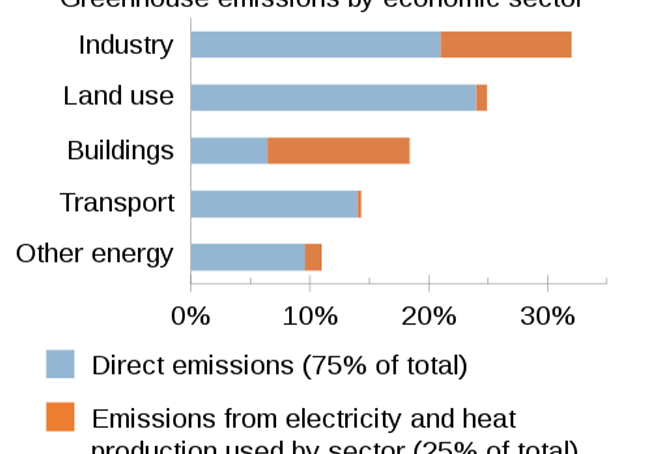
Agriculture contributes towards climate change through anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions and by the conversion of non-agricultural land such as forests into agricultural land.[5][6] In 2010, agriculture, forestry and land-use change were estimated to contribute 20–25% of global annual emissions.
In 2020, the European Union’s Scientific Advice Mechanism estimated that the food system as a whole contributed 37% of total greenhouse gas emissions, and that this figure was on course to increase by 30–40% by 2050 due to population growth and dietary change.
A range of policies can reduce the risk of negative climate change impacts on agriculture and greenhouse gas emissions from the agriculture sector.
