Particle Physics Experiments Reinforce Evidence of New Force of Nature

An experiment recently finished at the Fermi National Accelerator Lab (Fermilab) in Chicago has generated solid data recommending that a new force of nature may have been uncovered. If this result is inevitably confirmed, it would call for an alteration of the Criterion Model of particle physics, which presently presumes the existence of just 4 legislations that govern interactions at the subatomic degree: electromagnetism, gravity, the weak nuclear force, as well as the strong nuclear force. The evidently brand-new pressure of nature found in the Fermilab and also CERN’s Huge Hadron Collider is creating massive buzz in the world of quantum physics.
Proof Constructs for a 5th Pressure
The strange searching lately reported by the Fermilab are consistent with speculative outcomes attained at other high-energy physics research study facilities. Just last month, physicists operating at CERN’s Large Hadron Collider, the globe’s most powerful particle accelerator, asserted to have found proof of a 5th pressure at the workplace in nature as well as their outcomes match those attained at the Fermilab in essential ways.
Dr. Maggie Aderin-Pocock, the co-presenter of the BBC scientific research program Sky during the night, called the announcement from the Fermilab “fairly overwhelming.”
“It has the prospective to transform physics on its head,” Aderin-Pocock added. “We have a number of these enigmas that continue to be unsolved. As well as this could provide us the key answers to solve these enigmas.”
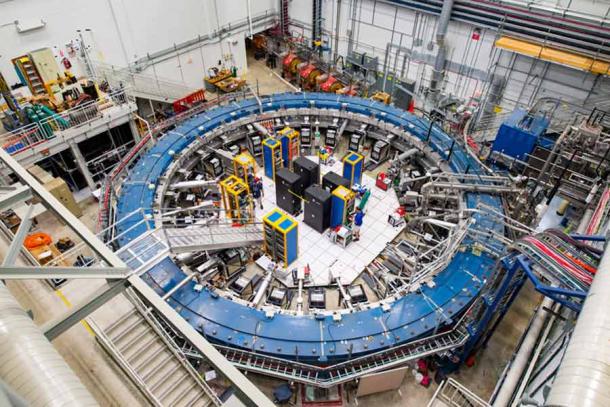

Odd Muon Wobble Results In New Pressure of Nature Discovery
The experiment that returned the possibly paradigm-shattering outcomes as well as the idea of a brand-new pressure of nature involved subatomic particles known as muons.
A muon is an adversely charged particle with a comparable profile to an electron (both are classified as leptons). However the mass of the muon is 200 times more than that of its angelic relative the electron. In nature, muons are generated by high-energy communications involving particles of matter, consisting of those that take place when particles in the Earth’s upper atmosphere are bombarded by cosmic rays.
Considering that they can likewise be reliably produced inside effective particle accelerators, muons make ideal experimental “subjects” for physicists studying the nature of truth and those searching for new forces of nature. Frequently, high-energy physics jobs are designed to look for or create anomalies, which then call for changes or addendums to recognized scientific laws or concepts.
In the Fermilab Muon-2 experiment, muons were sped up around a 45-foot (14-meter) ring, prior to being travelled through a magnetic field. Muons traveling via such a field must wobble at a specific rate, in accordance with forecasts derived from conventional four-force interactions (calculated with the effects of electromagnetism, gravity, the weak nuclear force, and the strong nuclear force.) But the muon experiment suggests a 5th pressure of nature.
To the surprise as well as pleasure of the Fermilab physicists, measurements of the muons in this experiment showed they were wobbling much more swiftly than expected. This indicates a few other pressure of nature must have been at job that affected muon wobble prices. As a result, in this speculative environment, a brand-new and formerly undetected force of nature would be one of the most logical means of explaining the muon wobble incongruity.
According to present estimations, there is a one in 40,000 opportunity that this result could be an analytical fluke. While this might appear outstanding, researchers are conservative relative to such matters, as well as the customized is to not to classify a new finding as a true discovery till the possibility of a coincidence can be decreased to simply one in 3.5 million.
Much more information is needed to reach a clear-cut final thought. But one knowledgeable source is overflowing with optimism. “My Spidey feeling is prickling and telling me that this is most likely to be genuine,” said loudly Ben Allanach, a professor of academic physics at Cambridge College that was not straight associated with the experiment. “I have been looking all my career for pressures and also bits beyond what we understand currently, and this is it. This is the minute that I have been awaiting and I’m not obtaining a lot of sleep because I’m also thrilled.”
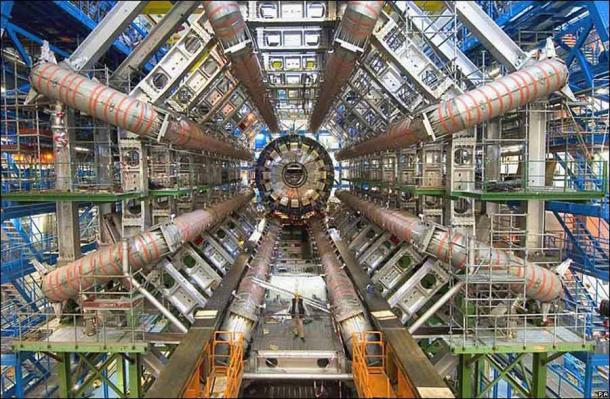
CERN’s Muon Anomalies Add More Fuel to the Fire
It was less than 3 weeks ago that physicists designated to CERN’s Large Hadron Collider issued their very own news asserting the feasible presence of a fifth subatomic force, which was likewise influenced by the outcomes of an experiment that involved muons.
In this instance, it was mysterious incongruities in quark degeneration rates that produced enjoyment. Quarks are the fundamental building blocks that make up particles like protons as well as neutrons, and also in particular situations they can degeneration right into negatively-charged leptons (electrons and also muons).
Under the Criterion Model of quantum physics, all quarks that undertake this sort of degeneration need to produce equivalent varieties of electrons and muons. However a new quark found by CERN scientists in 2014, called the charm quark, seemed to be generating much less muons than anticipated when being kept track of.
In 2019, CERN scientists working at the Huge Hadron Collider created experimental methods that could confirm definitively whether or not this abnormality was real. After greater than a year of pouring over the outcomes, the researchers finally provided their outcomes to the general public last month.
Validating their preliminary discovery, they discovered that beauty quarks in decay were creating even more electrons than muons at a price of 100-to-85. This diversion from Criterion Model predictions can not be clarified under the known legislations of physics, leading the CERN professionals in conclusion that one more unidentified pressure of nature was changing beauty quark habits.
“This force would be exceptionally weak, which is why we haven’t seen any kind of indicators of it until now, and would interact with electrons and muons in a different way,” scientists associated with the experiment told job interviewers from the podcast The Discussion Weekly.
The CERN researchers think that an academic fundamental particle called “Z prime” may be responsible for the outcomes they determined. This supernatural entity would be in charge of sending the new pressure between even more conventional particles of matter, in formerly undetected and unforeseen ways.

The Race gets on and Scientific Research Might Never Coincide
With revolutionary changes in our understanding of physics coming up, experimenters at high-energy laboratories around the world will certainly be looking for to get in on the action.
“The race is actually on currently to try and also get among these experiments to actually get the evidence that this truly is something brand-new,” stated Dr. Mitesh Patel, an Imperial University of London physicist who was involved in the Big Hadron Collider experiment. “That will take a lot more information and also even more dimensions and ideally reveal evidence that these impacts are actual.”
While significant work still needs to be done, it likely won’t take long for the pertinent study to start, in several areas. If indeed the laws of physics will change, that adjustment may happen in the really near future.
