Meteorite contains the oldest material on Earth: 7-billion-year-old stardust
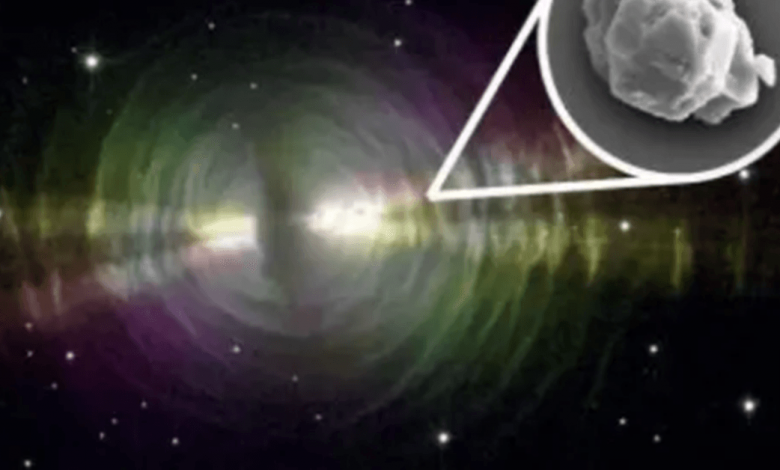

Researchers just found the Planet’s earliest product: 7 billion-year-old stardust preserved in a large, tough meteorite that impacted our earth 50 years back.
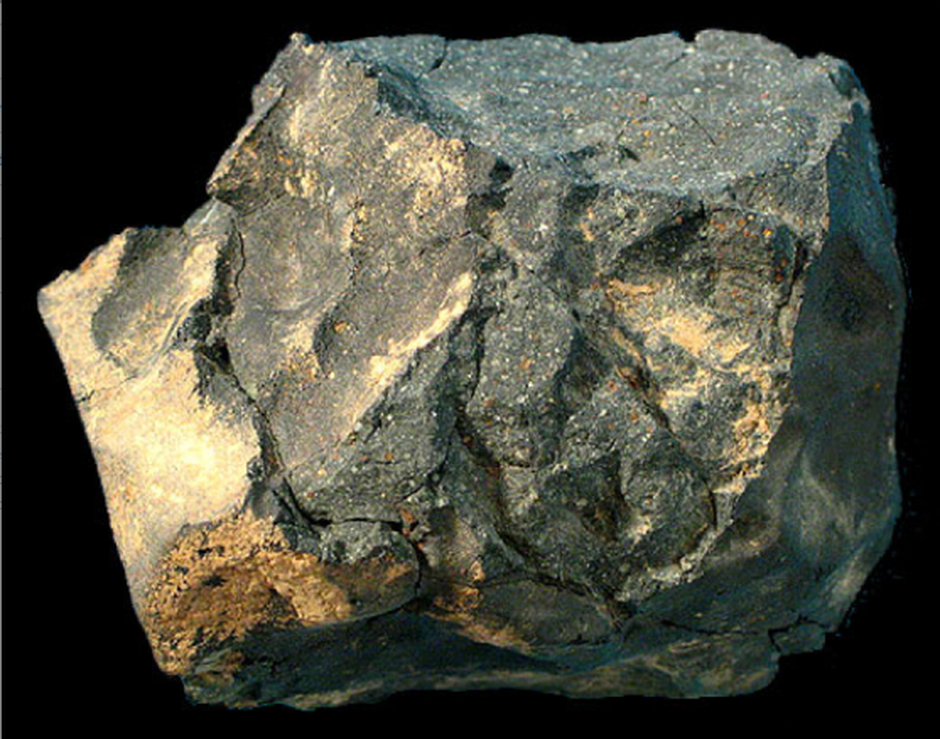
Stars live. They form when particles of dirt as well as gas taking a trip with area collide, collapsing and heating up. They blaze for millions to billions of years before dying. When celebrities pass away, they launch the particles created in their winds right into space, where they ultimately create new celebrities, along with new worlds, moons, and also meteorites. And also scientists have revealed stardust that developed 5 to 7 billion years back in a meteorite that collapsed in Australia fifty years back– the oldest strong substance ever detected on Earth.

This exploration adds fuel to a disagreement among researchers over whether new celebrities originate at a constant pace or if the number of brand-new stars differs with time. “Some believe that the galaxy’s star manufacturing price is constant,” Hell discusses. “However, owing to these grains, researchers now have direct evidence from meteorites suggesting a time of increased star development in our galaxy 7 billion years back. This is an essential verdict from our investigation.”
Hell stresses that this is not the initial surprise exploration made by his team. As a side note to the main research concerns, the scientists discovered that presolar grains typically wander with room locked together in enormous collections, “like granola,” adds Hell. “No one envisioned this would certainly be practical on that particular range.”
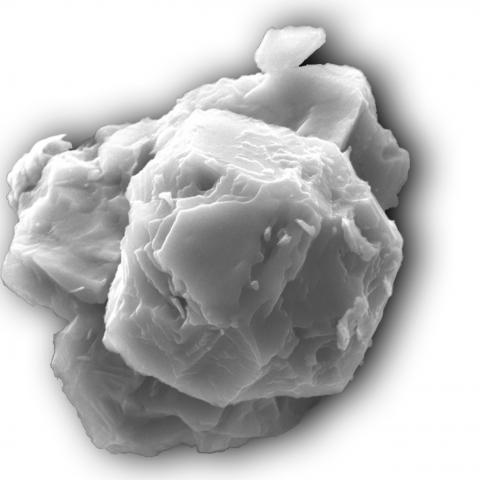
Heck observes that there are still a lifetime’s worth of unanswered problems on presolar grains and the early Planetary system. “I want there were even more individuals working on it to have a better understanding of our own galaxy, the Galaxy,” he adds.
The Area Gallery, the College of Chicago, the Lawrence Livermore National Research Laboratory, Washington College, Harvard Medical Institution, ETH Zurich, and the Australian National College all added to this job. The Field Gallery’s Science and also Scholarship Funding Committee received funding from NASA, the TAWANI Structure, the National Scientific Research Foundation, the Department of Energy, the Swiss National Scientific Research Structure, the Brazilian National Council for Scientific and also Technological Growth, and the Swiss National Science Structure.
