Cell membrane
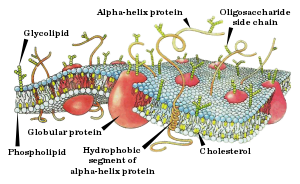
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment (the extracellular space) which protects the cell from its environment.[1][2] The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer, including cholesterols (a lipid component) that sit between phospholipids to maintain their fluidity at various temperatures. The membrane also contains membrane proteins, including integral proteins that go across the membrane serving as membrane transporters, and peripheral proteins that loosely attach to the outer (peripheral) side of the cell membrane, acting as enzymes shaping the cell.[3] The cell membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of cells and organelles. In this way, it is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules.[4] In addition, cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, the carbohydrate layer called the glycocalyx, and the intracellular network of protein fibers called the cytoskeleton. In the field of synthetic biology, cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.[5][6][7][8]
While Robert Hooke’s discovery of cells in 1665 led to the proposal of the Cell Theory, Hooke misled the cell membrane theory that all cells contained a hard cell wall since only plant cells could be observed at the time.[9] Microscopists focused on the cell wall for well over 150 years until advances in microscopy were made. In the early 19th century, cells were recognized as being separate entities, unconnected, and bound by individual cell walls after it was found that plant cells could be separated. This theory extended to include animal cells to suggest a universal mechanism for cell protection and development. By the second half of the 19th century, microscopy was still not advanced enough to make a distinction between cell membranes and cell walls. However, some microscopists correctly identified at this time that while invisible, it could be inferred that cell membranes existed in animal cells due to intracellular movement of components internally but not externally and that membranes were not the equivalent of a cell wall to plant cell. It was also inferred that cell membranes were not vital components to all cells. Many refuted the existence of a cell membrane still towards the end of the 19th century. In 1890, an update to the Cell Theory stated that cell membranes existed, but were merely secondary structures. It was not until later studies with osmosis and permeability that cell membranes gained more recognition.[9] In 1895, Ernest Overton proposed that cell membranes were made of lipids.[10]
The lipid bilayer hypothesis, proposed in 1925 by Gorter and Grendel,[11] created speculation to the description of the cell membrane bilayer structure based on crystallographic studies and soap bubble observations. In an attempt to accept or reject the hypothesis, researchers measured membrane thickness.[9] In 1925 it was determined by Fricke that the thickness of erythrocyte and yeast cell membranes ranged between 3.3 and 4 nm, a thickness compatible with a lipid monolayer. The choice of the dielectric constant used in these studies was called into question but future tests could not disprove the results of the initial experiment. Independently, the leptoscope was invented in order to measure very thin membranes by comparing the intensity of light reflected from a sample to the intensity of a membrane standard of known thickness. The instrument could resolve thicknesses that depended on pH measurements and the presence of membrane proteins that ranged from 8.6 to 23.2 nm, with the lower measurements supporting the lipid bilayer hypothesis. Later in the 1930s, the membrane structure model developed in general agreement to be the paucimolecular model of Davson and Danielli (1935). This model was based on studies of surface tension between oils and echinoderm eggs. Since the surface tension values appeared to be much lower than would be expected for an oil–water interface, it was assumed that some substance was responsible for lowering the interfacial tensions in the surface of cells. It was suggested that a lipid bilayer was in between two thin protein layers. The paucimolecular model immediately became popular and it dominated cell membrane studies for the following 30 years, until it became rivaled by the fluid mosaic model of Singer and Nicolson (1972).[12][9]
