Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
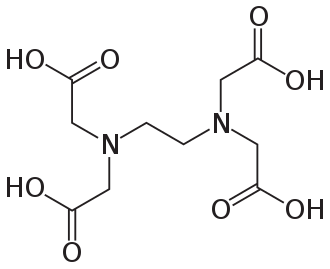
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) is an aminopolycarboxylic acid with the formula [CH2N(CH2CO2H)2]2. This white, water-soluble solid is widely used to bind to iron and calcium ions. It binds these ions as a hexadentate (“six-toothed”) chelating agent. EDTA is produced as several salts, notably disodium EDTA, sodium calcium edetate, and tetrasodium EDTA.[4]
In industry, EDTA is mainly used to sequester metal ions in aqueous solution. In the textile industry, it prevents metal ion impurities from modifying colours of dyed products. In the pulp and paper industry, EDTA inhibits the ability of metal ions, especially Mn2+, from catalysing the disproportionation of hydrogen peroxide, which is used in chlorine-free bleaching. In a similar manner, EDTA is added to some food as a preservative or stabiliser to prevent catalytic oxidative decolouration, which is catalysed by metal ions.[5] In soft drinks containing ascorbic acid and sodium benzoate, EDTA mitigates formation of benzene (a carcinogen).[6]
The reduction of water hardness in laundry applications and the dissolution of scale in boilers both rely on EDTA and related complexants to bind Ca2+, Mg2+, as well as other metal ions. Once bound to EDTA, these metal centres tend not to form precipitates or to interfere with the action of the soaps and detergents. For similar reasons, cleaning solutions often contain EDTA. In a similar manner EDTA is used in the cement industry for the determination of free lime and free magnesia in cement and clinkers.[7][page needed]
The solubilisation of Fe3+ ions at or below near neutral pH can be accomplished using EDTA. This property is useful in agriculture including hydroponics. However, given the pH dependence of ligand formation, EDTA is not helpful for improving iron solubility in above neutral soils.[8] Otherwise, at near-neutral pH and above, iron(III) forms insoluble salts, which are less bioavailable to susceptible plant species. Aqueous [Fe(EDTA)]− is used for removing (“scrubbing”) hydrogen sulfide from gas streams. This conversion is achieved by oxidising the hydrogen sulfide to elemental sulfur, which is non-volatile:
